Skin & Hair Care Clinic
Embrace radiant, healthy skin on every step of your journey with Shepperton Skin & Hair Care Clinic. We provide personalised skincare treatment and products tailored to your skin type, concerns, and needs, ensuring the care you need for a truly radiant glow.
Your skin deserves special care
At Shepperton Skin Care Clinic, we understand that skincare is essential for every individual’s overall well-being and health. We offer comprehensive consultations to assess your unique skin needs and develop personalised treatment plans for a wide range of skin concerns, including eczema, acne, dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, cold sores, impetigo, hives, fungal infections and many more. We believe that healthy skin is a foundation for confidence and happiness.
Additionally, we provide specialised treatments for hair-related issues such as scalp psoriasis, dandruff, and hair loss, ensuring you receive holistic care for both your skin and hair. Our commitment is to empower you with tailored solutions that promote not just healthier skin, but a healthier, more vibrant you.

Our Skin Care services are for the following conditions
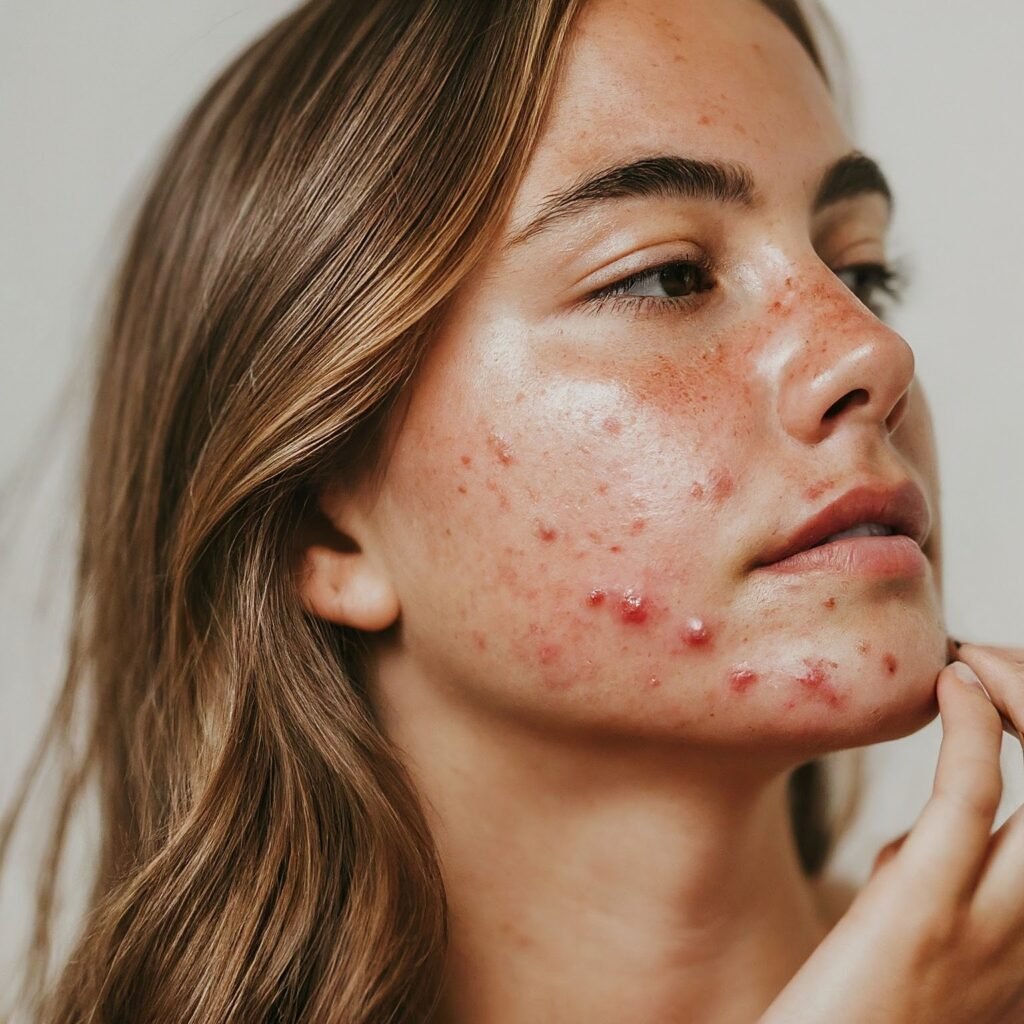
Acne
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions in the UK which affects most people at some point in their lives, however, severity and longevity of the condition varies. It is an inflammatory skin condition which leads to oily skin and the development of spots, including blackheads and whiteheads, on the skin. For many, acne only lasts for a short time during puberty when hormone levels are changing, however, for some, the effects of acne last much longer and can bring pain, scarring, and embarrassment. Acne is characterised by blackheads, whiteheads and cysts. It affects the greasy and hair-bearing areas such as the face, chest and back. Acne is caused by a combination of overactive grease-glands, hormones and bacterial infection. As with most skin conditions, acne can affect one’s confidence and cause low self-esteem.

Eczema
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterised by red, inflamed, itchy patches on the skin. It often begins in childhood but can affect individuals of all ages. Eczema is primarily caused by a weakened skin barrier that struggles to retain moisture and protect against environmental irritants, leading to dryness, irritation, and a susceptibility to allergens and bacteria. Flare-ups can be triggered by factors such as stress, temperature changes, harsh soaps, and certain fabrics. Although eczema is not contagious, it can significantly impact quality of life due to discomfort, disturbed sleep, and visible symptoms. Sometimes eczema causes severe discomfort disrupting sleep or daily activities, shows signs of infection (like streaks, pus, or yellow scabs), or persists despite self-care.

Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterised by persistent redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, red, pus-filled bumps on the face. Commonly affecting adults between the ages of 30 and 50, rosacea often begins with a tendency to flush or blush more easily than others. Over time, this redness can become more pronounced, especially across the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. The exact cause of rosacea is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. Common triggers that can exacerbate symptoms include exposure to sunlight, spicy foods, alcohol, stress, and extreme temperatures.

Dermatitis
Dermatitis is an inflammation of the skin that manifests as red, itchy, and often painful rashes. There are several types of dermatitis like atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis. The most common being contact dermatitis, which occurs when the skin reacts to allergens or irritants, and atopic dermatitis, which is often linked to other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever. Dermatitis can affect anyone, regardless of age, and may be triggered by various factors, including environmental allergens, chemicals, stress, or certain fabrics. Symptoms can vary from mild irritation to severe skin reactions, and the condition can be acute or chronic, with flare-ups that may cause discomfort and distress. Proper management of dermatitis to reduce inflammation and soothe itching is crucial to improving skin health and quality of life.
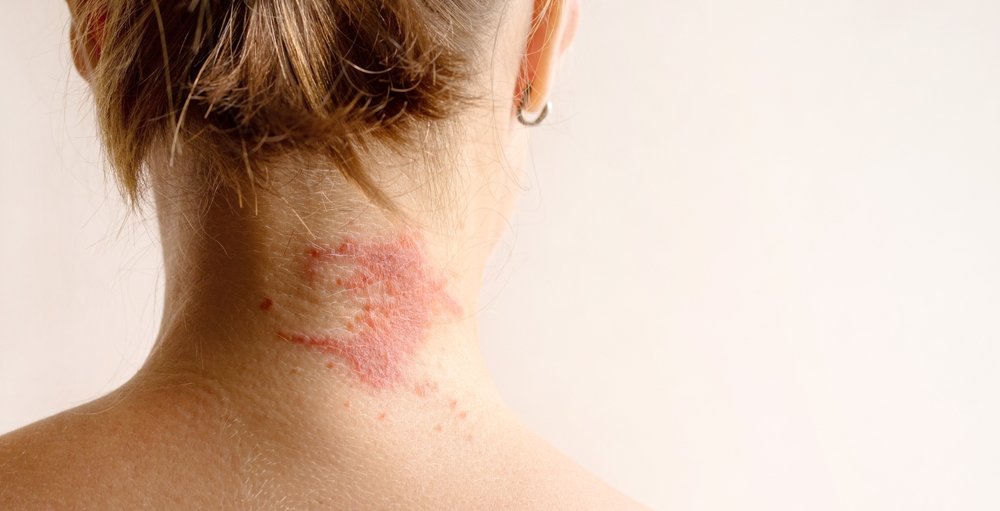
Hives
Hives, also known as urticaria, are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can vary in size and appear in clusters or as single spots. They are a common allergic reaction and can be triggered by a variety of factors, including foods, medications, insect stings, stress, or exposure to certain environmental elements. Hives often develop quickly and can fade in one area while appearing in another, making them particularly unpredictable. They may be accompanied by symptoms like swelling, especially around the eyes and lips, and can cause significant discomfort. While acute hives usually resolve within a few hours to a few days, chronic hives can persist for weeks or even months. Identifying and avoiding triggers is essential in managing hives effectively and preventing future outbreaks.

Impetigo
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that primarily affects children but can also occur in adults. Characterized by red sores or blisters, it often starts around the nose and mouth but can spread to other areas of the body through direct contact or by touching contaminated surfaces. The sores typically burst, ooze, and form a yellowish-brown crust, giving the skin a distinctive appearance. Impetigo is most caused by either Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria and can be triggered by minor skin injuries, insect bites, or conditions that break the skin barrier. While impetigo is generally not serious, it can be uncomfortable and lead to complications if left untreated. Prompt treatment with topical or oral antibiotics is essential to alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of spreading the infection, and promote healing. Good hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing and avoiding sharing personal items, are crucial in preventing the spread of impetigo.

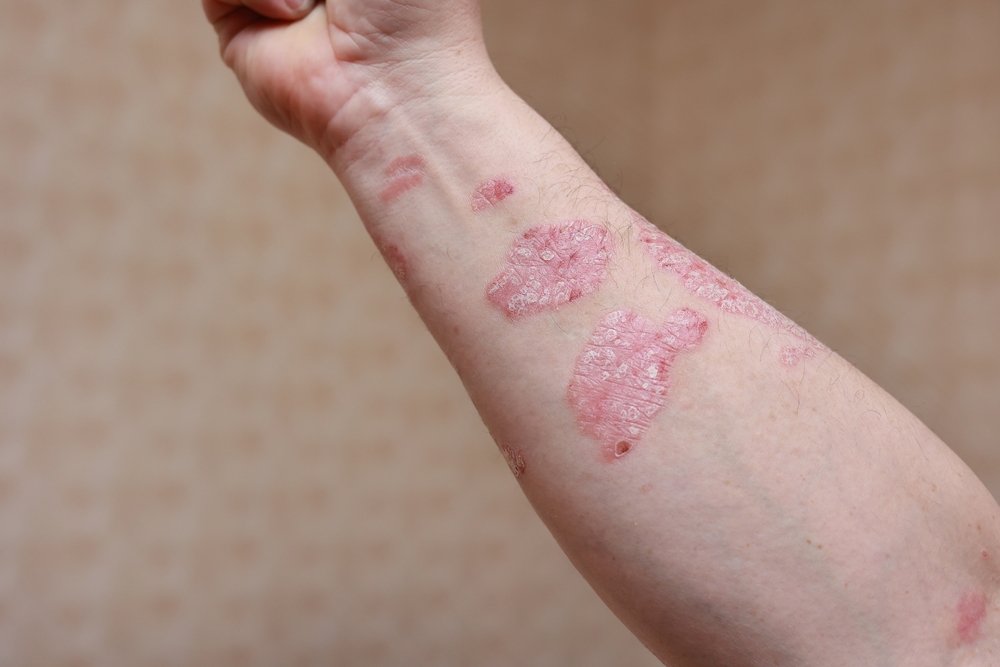
Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin condition characterised by the rapid overproduction of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, red, scaly patches known as plaques. These plaques typically develop on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back but can appear anywhere on the body. The condition often causes significant itching and discomfort, and the plaques may crack and bleed, further complicating the symptoms. The exact cause of plaque psoriasis is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Triggers can include stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications. Managing plaque psoriasis is essential for improving quality of life and minimizing the physical and emotional impact of the condition.
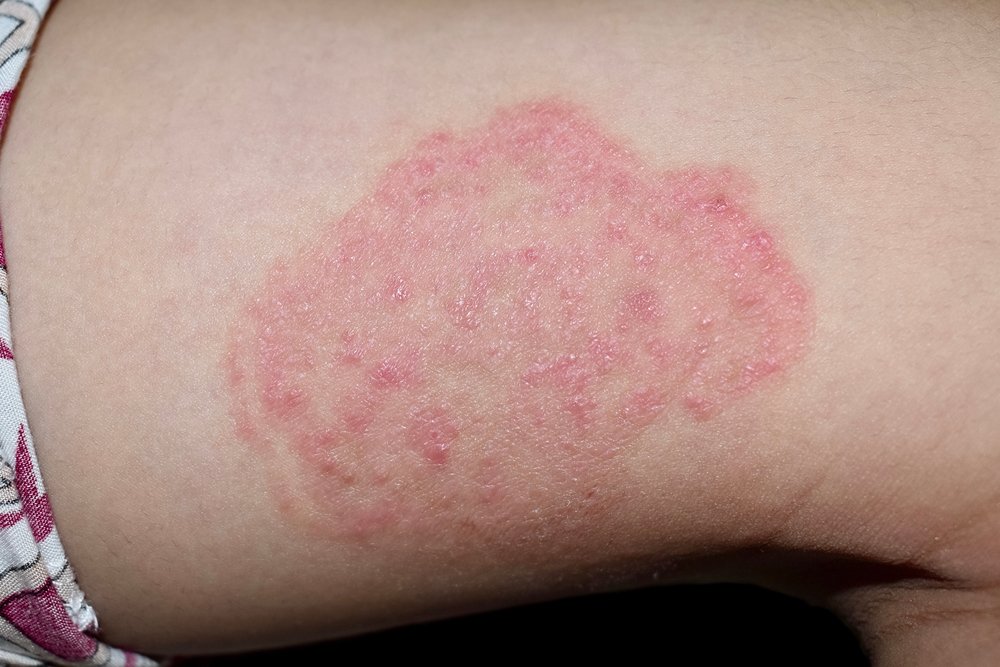
Fungal infections
Fungal infections, also known as mycoses, are caused by the overgrowth of fungi on or within the body and can affect various areas, including the skin, nails, and mucous membranes. Common types of fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections, each caused by different types of fungi. Symptoms often vary depending on the infection but can include redness, itching, flaking skin, and in some cases, painful swelling or discharge. Fungal infections thrive in warm, moist environments, making them more prevalent in areas like the feet, groin, and underarms. While many fungal infections are mild and easily treatable with antifungal medications, some can become chronic or recurrent, requiring prolonged treatment and lifestyle adjustments to prevent reinfection. Good hygiene practices, such as keeping the skin dry and clean, avoiding tight clothing, and not sharing personal items, are crucial in preventing the spread of fungal infections and maintaining overall skin health.
Cold sores
Cold sores, also known as fever blisters, are small, painful blisters that typically appear on or around the lips and mouth, caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). The initial infection can occur during childhood or adolescence, often manifesting as flu-like symptoms, followed by the formation of blisters. Once contracted, the virus remains dormant in the body and can reactivate due to various triggers, including stress, illness, fatigue, hormonal changes, or sun exposure. Cold sores usually start with a tingling or itching sensation before developing into fluid-filled blisters that eventually crust over and heal within one to two weeks. While cold sores are generally not serious, they can be uncomfortable and embarrassing, and they are highly contagious, especially during an outbreak. Preventive measures, such as avoiding known triggers and practicing good hygiene, can help manage and minimize the frequency of cold sore outbreaks.

Facial hirsutism
Facial hirsutism is a condition characterised by the excessive growth of coarse, dark hair on the chin, upper lip, and cheeks. This condition is often caused by an imbalance in hormones, particularly an excess of androgens (male hormones) in women, which can result from various factors, including polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hormonal disorders, or certain medications. The emotional and psychological impact of hirsutism can be significant, leading to feelings of embarrassment, low self-esteem, and anxiety about appearance. Treatment options vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition and may include lifestyle changes with healthy diet and regular exercise and hormonal therapy. It’s essential for individuals experiencing facial hirsutism to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment to manage the condition effectively.

Thrush
Thrush, also known as oral candidiasis, is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida species, particularly Candida albicans, in the mouth and throat. This condition is characterized by white patches or lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, and throat, which can be painful and may cause discomfort during eating or swallowing. Thrush commonly occurs in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as infants, the elderly, and those with certain medical conditions like diabetes or HIV/AIDS. It can also be triggered by factors such as antibiotic use, hormonal changes, and poor oral hygiene. While thrush is not usually serious, it can be bothersome and may lead to more severe health issues if left untreated. In some cases, addressing underlying conditions and lifestyle changes may also be necessary to reduce the risk of future outbreaks.

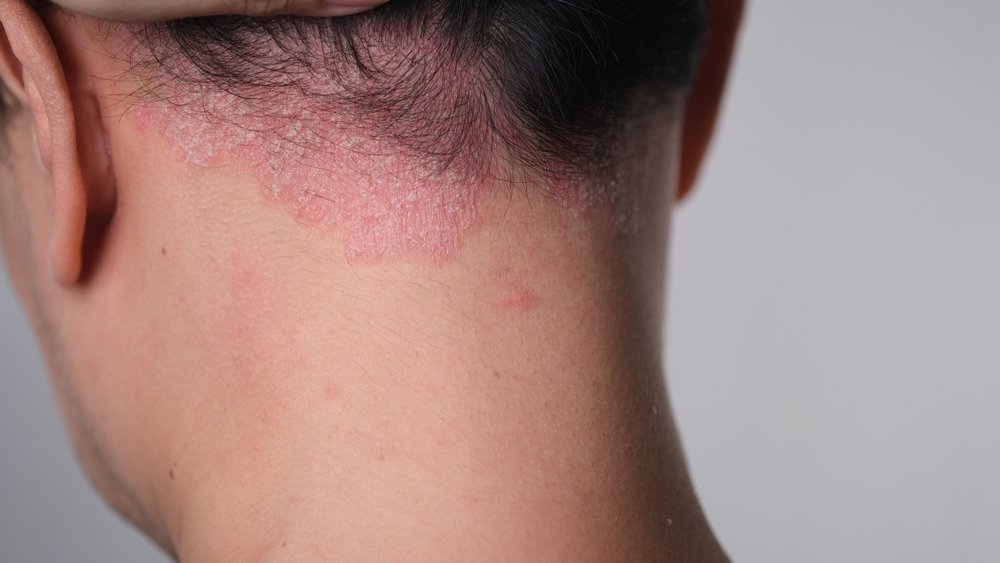
Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterised by the rapid overproduction of skin cells on the scalp, leading to the formation of red, itchy patches covered with silvery-white scales. These plaques can vary in severity, from mild flaking to severe, crusted lesions that may extend beyond the hairline to the forehead, neck, and ears. While the exact cause of scalp psoriasis is not fully understood, it is believed to be linked to genetic factors, immune system dysfunction, and environmental triggers such as stress, infections, and skin injuries. Symptoms often include itching, burning, and discomfort, which can be exacerbated by dry weather or harsh hair products. Managing scalp psoriasis is essential not only for alleviating physical symptoms but also for improving quality of life and self-esteem, as the visible nature of the condition can lead to emotional distress.
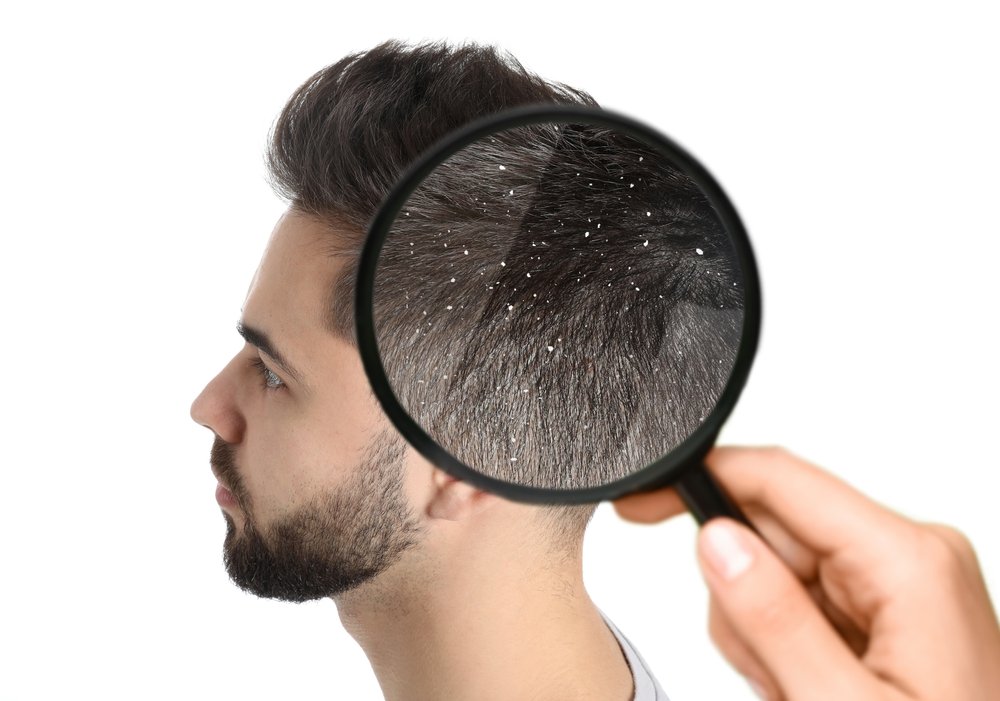
Dandruff
Dandruff is a common scalp condition characterised by the shedding of dead skin cells, leading to visible flakes on the hair and shoulders, often accompanied by itching and irritation. While it is not a serious health concern, dandruff can be bothersome and affect an individual’s self-esteem and comfort. The exact cause of dandruff can vary, but it is often linked to factors such as dry skin, seborrheic dermatitis, fungal infections (like Malassezia), sensitivity to hair products, and even stress. People with oily skin or certain skin conditions may be more prone to dandruff. Treatment typically involves the use of anti-dandruff shampoos which help reduce flaking and inflammation. Additionally, maintaining a healthy scalp through proper hygiene, balanced nutrition, and minimizing stress can contribute to dandruff prevention. If dandruff persists despite treatment, it is recommended to explore underlying causes and effective management strategies.

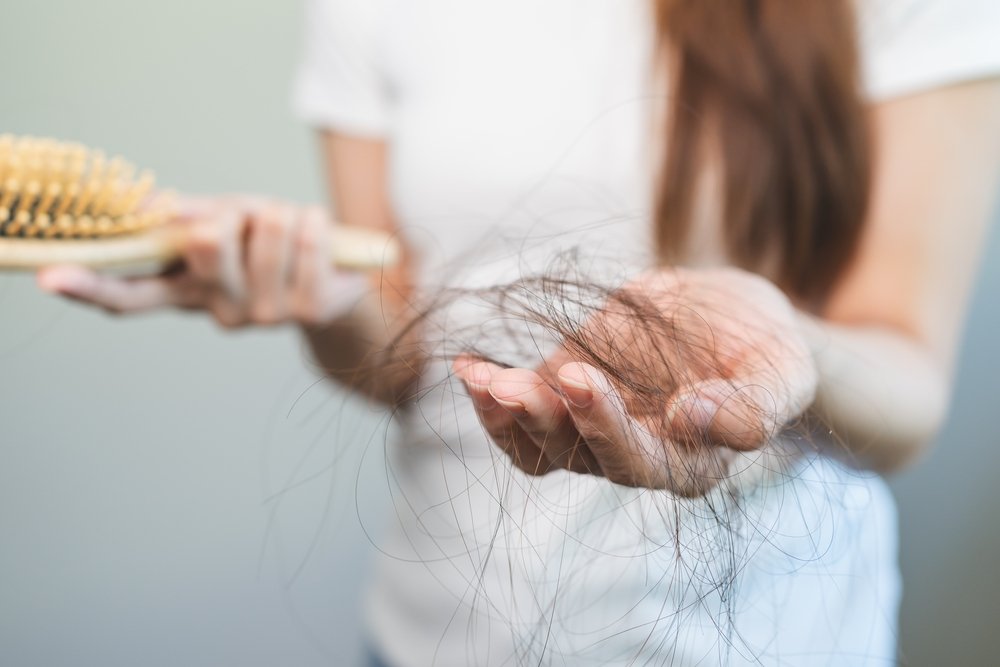
Hair loss
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide and can occur for various reasons, including genetic factors, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and environmental influences. It can manifest in different forms, such as thinning hair, bald patches, or complete hair loss on the scalp or body. Male and female pattern baldness, which is primarily driven by genetics and hormones, is one of the most prevalent types of hair loss. Other causes may include stress, nutritional deficiencies, certain medications, autoimmune diseases, and scalp infections. The emotional and psychological impact of hair loss can be significant, leading to feelings of self-consciousness and lowered self-esteem. Various treatment options are available, ranging from topical treatments to oral medications as well as lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and hair restoration techniques. It is essential for individuals experiencing hair loss to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan tailored to their specific needs.

Book your Skin & Hair Care Clinic Today
FAQ
What services does the Skin and Hair Care Clinic at Trio Pharmacy offer?
We provide a range of services, including skin consultations, treatment for acne, eczema, psoriasis, hair loss, scalp conditions, anti-aging solutions, and more.
Do I need an appointment to visit the clinic?
Yes, we recommend booking an appointment to ensure a dedicated consultation with our specialist team.
Can I get advice on managing acne-prone skin?
Absolutely! Our experts provide personalised skincare plans and recommend suitable treatments for acne and other skin conditions.
Do you offer treatments for hair loss?
Yes, we provide consultations for hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments, including topical solutions, oral medications, or lifestyle changes.
Are the treatments safe for sensitive skin?
Yes, our experts carefully evaluate your skin type and condition to recommend safe and effective treatments, even for sensitive skin.
Can I purchase skincare products at Trio Pharmacy?
Yes, we stock a range of dermatologist-approved skincare products suitable for various skin types and conditions.
Do you provide anti-aging treatments?
Yes, we offer anti-aging solutions, including skincare advice, advanced products, and treatment recommendations tailored to your needs.
How long does a consultation take?
A typical consultation lasts around 15–20 minutes, depending on the complexity of your concerns.
Do you treat scalp conditions like dandruff or psoriasis?
Yes, our clinic offers treatments for a variety of scalp conditions, including dandruff, psoriasis, and seborrheic dermatitis.
How do I book an appointment at the Skin and Hair Care Clinic?
You can book an appointment online via our website or call Trio Pharmacy directly to schedule your visit.

